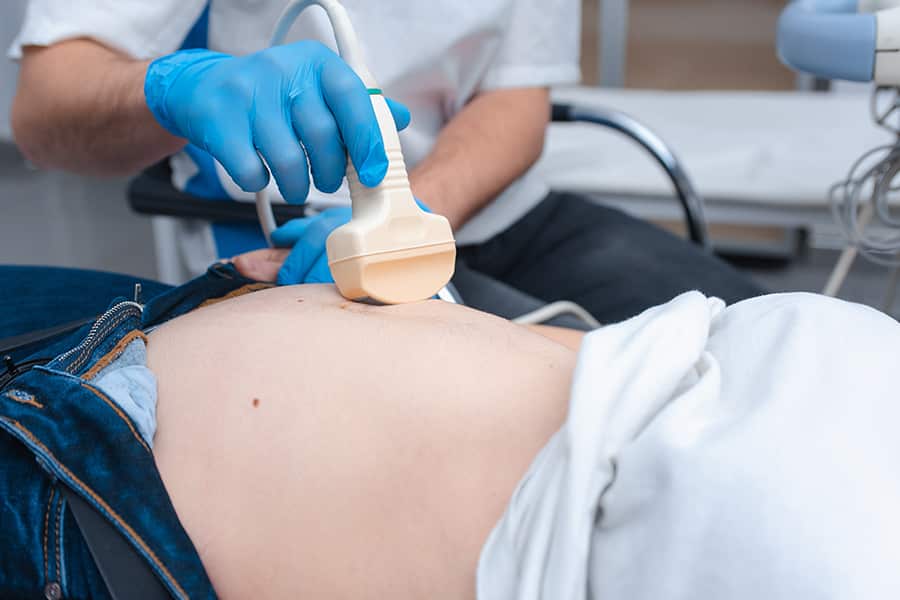
Ultrasound scans are a vital part of prenatal care, providing valuable information about the health of the fetus and the progress of the pregnancy. The frequency of ultrasounds can vary based on various factors including maternal health, the progress of the pregnancy, and medical recommendations. This article explores how often you should expect to have ultrasound scans during pregnancy and how certain conditions might impact those recommendations.
Understanding Ultrasound Scans
Before diving into the frequency of ultrasounds, it is essential to understand what scans are and why they are important:
- Purpose of Ultrasound Scans
- Ultrasound scans use sound waves to create images of the baby in the womb. These images help healthcare providers assess the baby’s development, detect abnormalities, monitor fetal health, and determine the position of the fetus and placenta.
- Types of Ultrasound Scans
- Transvaginal Ultrasound: Used in early pregnancy to get a clear view of the uterus and fetus. The ultrasound transducer is carefully introduced through the vagina.
- Abdominal Ultrasound: More common and used throughout pregnancy to examine the baby’s growth and development. The ultrasound transducer is applied to the skin of the abdomen.
- Specialized Ultrasound: Used to closely examine suspected fetal anomalies or complications.
General Recommendations for Ultrasound Frequency
- First Trimester
- Dating and Viability Ultrasound (6-9 weeks): Confirms the pregnancy is viable, checks on the location of the embryo in the uterus, and determines the number of embryos. It also provides a precise gestational age which is crucial for the timing of future prenatal tests and the due date.
- Nuchal Translucency Ultrasound (around 12 weeks): Part of screening for Down’s syndrome and other chromosomal abnormalities.
- Second Trimester
- Anatomy Scan (18-22 weeks): This detailed ultrasound checks the baby’s organs and body systems to ensure everything is developing normally. It can also reveal the baby’s sex if not already known.
- Third Trimester
- Growth Scans (as needed after 28 weeks): These are often performed in pregnancies with risk factors for fetal growth issues but may be offered routinely in some practices to monitor size and amniotic fluid levels.
Factors Influencing the Frequency of Ultrasounds
While the above outlines a typical scenario, many factors can necessitate additional scans:
- Multiple Pregnancies
- Women carrying twins or more will generally have more frequent ultrasounds to monitor the health and development of each fetus, as well as potential complications like Twin-to-Twin Transfusion Syndrome (TTTS).
- High-Risk Pregnancies
- Conditions such as preeclampsia, gestational diabetes, or a history of complications in previous pregnancies may require more frequent monitoring to ensure both the mother’s and baby’s health remain optimal.
- Previous Miscarriages or Pregnancy Losses
- Additional scans may be recommended for women with a history of miscarriage or pregnancy loss to monitor the pregnancy’s progress and provide reassurance.
- Detected Abnormalities
- If any abnormalities are detected during routine scans, more frequent ultrasounds may be necessary to closely monitor the fetus’s condition and development.
- Maternal Health Issues
- Health issues in the mother, like hypertension or diabetes, might also warrant additional scans to ensure the pregnancy is progressing without complications.

How to Approach Ultrasound Frequency
- Follow Medical Advice
- Always follow the guidance of your healthcare provider regarding how often you should have an ultrasound. They will make recommendations based on the most current clinical guidelines and your individual health needs.
- Balanced Perspective
- While it is exciting to see your baby through ultrasound images, it is important to balance this with medical necessity. Excessive exposure to ultrasound without clinical justification is generally avoided.
- Insurance and Cost Considerations
- Consider your health insurance coverage and other related costs. Some insurance plans limit the number of covered ultrasounds unless they are deemed medically necessary.
The frequency of ultrasound scans during pregnancy can vary widely depending on individual circumstances and medical advice. While typical pregnancies might require only a few key scans, factors like multiple pregnancies, high-risk conditions, and previous pregnancy issues might necessitate more frequent monitoring. It is essential for expectant mothers to maintain open communication with their healthcare provider to ensure that they receive the appropriate level of prenatal care, balancing the joy of seeing their developing baby with the practical aspects of medical and health considerations. Always rely on professional guidance to determine the best ultrasound schedule for your pregnancy.
This information is presented as a general guide on how often you should get an ultrasound during pregnancy. It is for informational purposes only. The information provided is not intended to be the only information available on how often you should get an ultrasound during pregnancy. The material provided is not expected to be a substitute for advice or information from your physician or health care provider.
If you have any questions, concerns, fears, apprehensions, unease, or worry about how often you should get an ultrasound during pregnancy contact your health care provider immediately.